Coming soon for patients taking XARELTO® (rivaroxaban): Janssen CarePath for XARELTO® and Janssen Select will transition to XARELTO withMe. We are simplifying access to our patient support in one location with a new name and look. Savings card and coverage gap benefits will not change.
What is CAD?
CAD is a progressive condition that is a result of plaque buildup that blocks your arteries from supplying blood to your heart. When your heart does not get proper blood flow, it can no longer pump the amount of oxygen and nutrients your muscles need to keep you healthy and active.
Understanding CAD could help lower your risk for blood clots
People with CAD have a high risk for blood clots due to a rupture of plaque in the arteries.
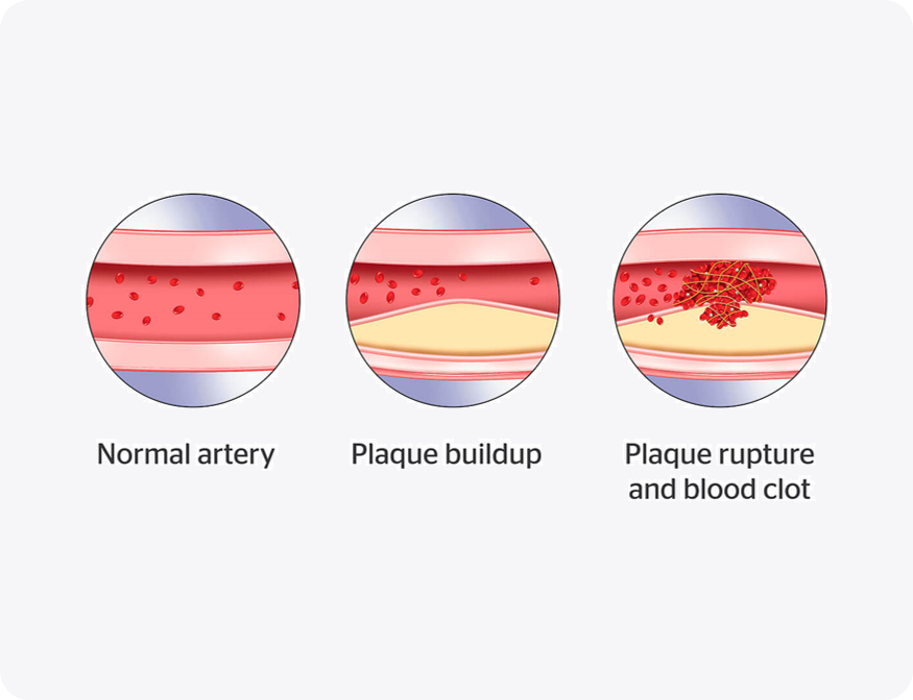
When plaque ruptures and forms a blood clot, it can cut off blood flow to your heart or brain and cause serious, life-threatening events:
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Cardiovascular death
Treatments for CAD
Common treatments for CAD include certain procedures to restore blood flow to your heart:
- Coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG)
- Angioplasty
- Cardiac rehabilitation
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
- Stent implantation
However, even with a procedure, you’re still at risk of blood clots that can cause a heart attack, stroke, or cardiovascular death. Your healthcare professional may prescribe medicines to help reduce your risk for blood clots. Although many people with CAD take only a daily aspirin, it may not be enough to reduce blood clot risk.
The role of blood thinners with aspirin
Your healthcare professional may prescribe a blood thinner—in addition to your daily aspirin—to help reduce your underlying risk for blood clots that can cause a heart attack, stroke, or cardiovascular death.
What’s next?
Read Learning About XARELTO® for more information about how XARELTO® works with low-dose aspirin* to help reduce your risk for life-threatening blood clots related to CAD.
*Low-dose aspirin = 75 mg–100 mg once daily.


